Liquefied natural gas power plant: A key role in providing sustainable electricity
With the increasing demand for energy and the need for diverse and relatively cleaner sources for electricity generation, natural gas has become one of the most important fuels in the world. “Liquefied Natural Gas” (LNG), which is natural gas that has been converted to a liquid state after a severe cooling process, reducing its volume by about 600 times, allows it to be transported over long distances by special ships. A liquefied natural gas power plant refers to a power plant that uses LNG as the main fuel for generating electrical energy. These power plants play an important role in energy security, power grid flexibility, and reducing pollution compared to traditional fossil fuels such as coal and oil. This article examines the performance, advantages, and role of this type of power plant in the energy system.
Liquefied natural gas power plant performance
The process of electricity generation in a liquefied natural gas power plant typically involves the following steps:
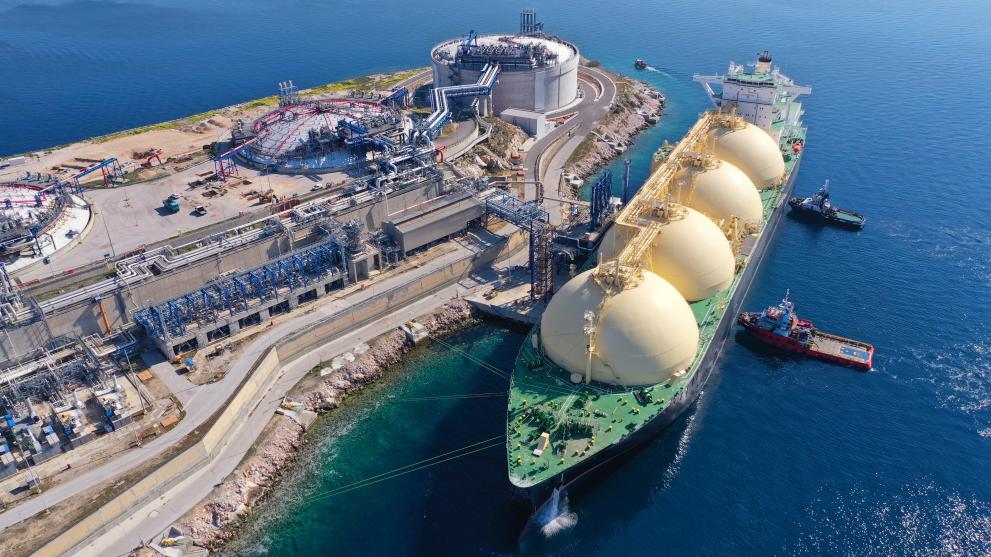
- Regasification: First, LNG is converted back from a liquid state to a gaseous state. This is usually done at LNG receiving terminals using heat exchangers. The required heat can be supplied from various sources such as seawater or even waste heat from industrial processes.
- Gas Transmission: The resulting natural gas is transferred to the power plant.
- Combustion and Mechanical Energy Generation: Natural gas is burned in the combustion chamber of a gas turbine. The resulting hot gases, with high pressure and speed, move the turbine blades. This mechanical energy is connected to a generator.
- Electricity Generation: The generator, by rotating with the turbine, converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Many liquefied natural gas power plants use combined cycle technology. In these power plants, the waste heat from the gas turbine is used to generate steam, and this steam drives a separate steam turbine that is connected to another generator. This configuration significantly increases the overall efficiency of the power plant.
Key Advantages of Liquefied Natural Gas Power Plants
Using LNG as fuel in power plants has several advantages:
- Flexibility and Security of Supply: The ability to transport LNG by sea reduces reliance on pipelines and increases fuel supply security for countries with limited pipeline access or those seeking to diversify their supply sources. This feature is important for liquefied natural gas power plants in remote areas or islands.
- Lower Emissions: The combustion of natural gas produces fewer carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter compared to coal and heavy oil. This helps improve air quality and reduce the impacts of climate change.
- High Efficiency (in Combined Cycle): Gas-fired combined cycle power plants (which can be fueled by LNG) are among the most efficient types of thermal power plants.
- Fast Start-up Time: Gas turbines used in Liquefied Natural Gas power plants can be started and stopped relatively quickly, making them suitable for responding to demand fluctuations (especially for covering peak consumption).
Challenges and disadvantages
Despite the advantages, the use of LNG also presents challenges:
- Infrastructure Cost: The construction of LNG receiving terminals and storage tanks requires significant initial investment.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Although lower than coal, the combustion of natural gas still leads to carbon dioxide emissions. Furthermore, methane (the primary component of natural gas) leakage throughout the LNG supply chain can have significant greenhouse effects.
- LNG Price: The price of LNG can be volatile in the global market, influenced by geopolitical factors and supply and demand dynamics.
The Role of Liquefied Natural Gas Power Plants in the Future of Energy
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) power plants play a crucial role in the energy transition era due to their flexibility and lower emissions compared to heavier fossil fuels. These plants can serve as reliable backups for variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. When the sun sets or the wind doesn’t blow, gas power plants can quickly come online, ensuring grid stability. In Iran, despite abundant natural gas resources, direct gas utilization via pipelines is more common. However, in regions where pipeline access is difficult, or for exporting electricity to other areas via LNG, the construction of LNG power plants could be considered.
Conclusion
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) power plants are a critical technology in the global energy landscape. By providing flexibility, supply security, and relatively lower emissions, these plants help countries meet their growing electricity demands while transitioning towards reduced carbon emissions. Although challenges such as infrastructure costs and greenhouse gas emissions persist, the role of these plants as a bridge in the transition towards a cleaner energy future is undeniable. Our specialists are with you at all stages of power plant construction.