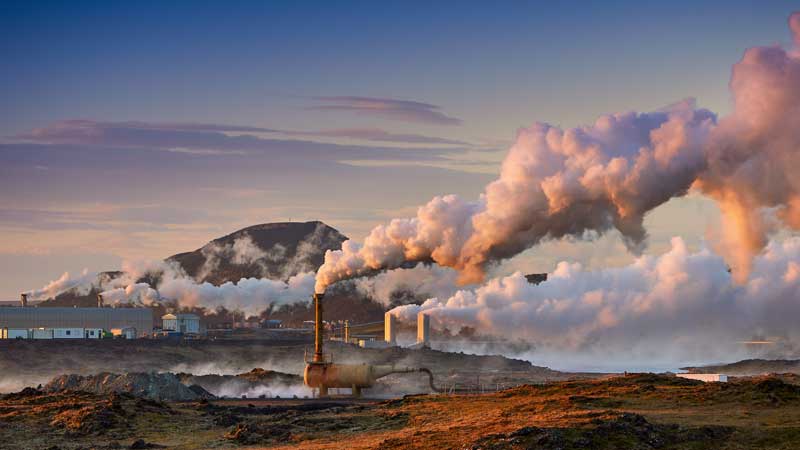
Electricity generation sources: A comprehensive look at types, advantages, and disadvantages.
The importance of electricity in modern life and the diversity of its generation sources.
Electricity is the vital artery of modern civilization. From lighting homes and streets to powering large industries and advanced technologies, everything depends on this form of energy. But how is this vital force produced? Electricity (energy) generation sources are very diverse, and each has its own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding these sources helps us to better comprehend the global energy system, the challenges ahead, and the path towards a more sustainable future. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the main types of electricity generation sources.
Fossil fuel sources: The traditional backbone of electricity generation.
For decades, fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas have been the primary sources of electricity generation worldwide. Due to their high energy density and relative ease of extraction and transportation, these resources have played a pivotal role in industrial development.
-
Thermal power plants:
- Coal: One of the oldest and most widely used fuels for electricity generation. In coal-fired power plants, coal is burned to convert water into steam. High-pressure steam turns turbines, and generators produce electricity.
- Natural gas: Burns cleaner than coal and is used in combined-cycle power plants, which have higher efficiency. Natural gas also produces steam by burning or directly drives gas turbines.
- Oil: Although used less than coal and natural gas in electricity generation, it is still used in some regions, especially for smaller power plants or during peak demand.
-
The advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels :
- Advantages: Relatively easy access (in the past), mature technology and existing infrastructure, ability to generate electricity on a large and stable scale.
- Disadvantages: Emission of large amounts of greenhouse gases (major cause of climate change), air pollution (particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides), limited and non-renewable resources, price fluctuations in global markets.
Renewable energy sources: A clean and sustainable future.
With increasing concerns about climate change and the limitations of fossil fuels, attention to renewable energy sources, which are derived from natural and inexhaustible resources, has significantly increased.
-
Hydropower (Hydroelectricity) :
- One of the oldest and largest renewable sources of electricity generation. It utilizes the force of moving water (usually behind dams) to spin turbines and produce electricity.
-
Wind power :
- Electricity is generated using wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy. Wind farms are built in windy areas.
-
Solar power :
- Electricity is produced using photovoltaic (PV) panels that directly convert sunlight into electricity, or with solar thermal systems that use the sun’s heat to produce steam and spin turbines.
-
Geothermal power :
- Geothermal energy utilizes the heat stored deep within the Earth. In this process, water or another fluid is pumped into the ground, the Earth’s heat warms it up, and then the steam or hot fluid is brought to the surface to turn turbines.
-
Biomass power :
- This method involves burning organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, or municipal solid waste to generate heat and steam. Biomass can also be converted into biofuels.
-
Tidal power :
- It uses the energy from the movement of tides or ocean waves to turn turbines and generate electricity. This technology is still in the early stages of large-scale development.
-
The overall advantages and disadvantages of renewable energies
- Variable Generation: These energy sources produce electricity variably, as their production depends on weather conditions.
- Large Space Requirement: Some of these sources (such as solar and wind) require a large space for equipment installation.
- High Initial Costs: These sources often have high initial costs for setup and the creation of necessary infrastructure.
- Need for Storage: These sources require advanced energy storage systems to ensure a stable supply of electricity.
- Geographical Dependency: The usability and exploitation of these sources heavily depend on the geographical location of the region.
Nuclear Energy: A powerful source with specific challenges
Nuclear energy uses the process of nuclear fission of heavy atoms (like uranium) to produce vast amounts of heat. This heat is used to produce steam and turn turbines.
-
Overall Process and It’s Position :
- In nuclear reactors, nuclear fission is carried out in a controlled manner. The resulting heat converts water into steam, and this steam rotates a turbine connected to a generator. Nuclear energy supplies about 10% of the world’s electricity and is active in over 30 countries.
-
Advantages and disadvantages :
- Advantages: Large-scale and stable electricity generation (24/7), no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, very high energy density.
- Disadvantages: Production of highly dangerous and long-lasting radioactive waste, safety concerns and risk of nuclear accidents, proliferation risks related to nuclear weapons, very high initial costs, and long construction times.
Comparison of Different Sources: Difficult Choices for the Future of Energy
The selection of an optimal combination of electricity generation sources for each country depends on multiple factors, including access to natural resources, economic conditions, environmental considerations, and network sustainability.
- Efficiency: Fossil and nuclear power plants can operate continuously at high capacity, whereas variable renewable sources require management and storage solutions.
- Cost: The initial construction costs of nuclear power plants and some renewable projects are high, but the operational costs of fossil fuels can be significant in the long run. Meanwhile, the costs of renewable technologies are decreasing.
- Environmental Impacts: Fossil fuels are a major cause of pollution and climate change, while renewable and nuclear sources (during operation) are considered cleaner. However, each has its own specific environmental challenges, such as nuclear waste or habitat impacts from large renewable projects.
Challenges and the Future of Energy Generation: Transitioning Towards Sustainability
The world is transitioning from an energy system based on fossil fuels to cleaner and more sustainable sources. This transition comes with significant challenges :
- Climate Change: The urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is increasing pressure to develop renewable sources more rapidly.
- Energy Security: Diversifying electricity generation sources leads to reduced dependence on fossil fuels and enhances energy security.
- Technological Development: Advances in energy storage technologies, smart grids, and new nuclear reactors are crucial for facilitating this transition.
- Infrastructure: There is a need for massive investment in electricity transmission and distribution infrastructure to adapt to variable renewable sources.
Conclusion: A combination of resources for a brighter future
No single source can meet all of the world’s energy needs on its own. The future of power generation will likely involve a mix of different resources, with the share of renewable energies increasing progressively. Smart management of this combination, investments in innovative technologies, and international collaborations are key to overcoming challenges and achieving a sustainable, reliable, and environmentally friendly energy system for future generations. Transitioning to cleaner sources is not only an environmental necessity but also an economic opportunity for innovation and growth.