Electricity generation through tides: A powerful and sustainable source
Among the diverse sources of renewable energy, tidal energy holds a special place due to its predictable nature and high power. Oceans and seas are a vast source of energy, and the regular movement of tides provides a unique opportunity for clean electricity generation. But how is electricity generated through tides, and what is its potential for the future of global energy?
What are tides and how do they generate energy?
It is a natural phenomenon that occurs due to the gravitational force of the moon and the sun on the waters of oceans and seas. Tides cause the water level to rise and fall along coastlines. This regular and powerful movement of water contains significant kinetic and potential energy that can be harnessed and converted into electrical energy.
Tides are a completely predictable phenomenon. The timing and height of tides can be predicted with high accuracy for years in advance, which makes tidal energy a reliable source for sustainable electricity generation.
Main methods of electricity generation from tides
Various technologies are used to harness tidal energy and convert it into electricity, each with its own advantages and challenges:
-
Tidal Barrages :
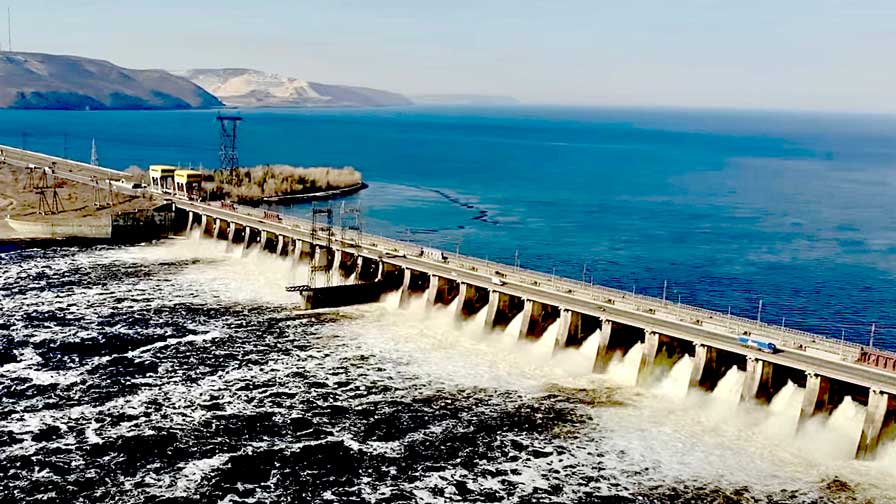
This method is similar to hydroelectric dams. A dam is built across the mouth of a bay or estuary with a high tidal range. During high tide (rising water), the dam’s gates are opened to allow water into the basin behind the dam. Then, the gates are closed. During low tide (falling water), a water level difference is created between the basin and the sea. Water flows through turbines installed in the dam towards the sea, causing the turbines to rotate and generate electricity. This method has the potential for large-scale electricity generation, but it involves high construction costs and can have significant environmental impacts on the region’s ecosystem.
-
Tidal Stream Generators :
This technology is similar to underwater wind turbines. Turbines are installed in areas with strong tidal currents on the seabed or suspended in the water. The water flow causes the turbine blades to rotate and generate electricity. This method does not require dam construction and has a lower environmental impact compared to tidal barrages. Installing and maintaining them in deeper marine environments can be challenging.
-
Tidal Lagoons :
This method is a combination of the previous two. A structure (usually circular or oval) is built in the sea, creating an artificial basin. This basin functions like tidal barrages, utilizing the water level difference between the inside of the lagoon and the sea to turn turbines and generate electricity. This method offers more flexibility in site selection and can have a lower environmental impact compared to large barrages.
Advantages of Tidal Energy
Using tides to generate electricity has significant advantages:
- High predictability: Unlike other renewable sources, the timing and amount of electricity generation from tides are completely predictable, which makes grid management easier.
- High energy density: Water is much denser than air, so even relatively slow water currents can produce significant energy.
- Sustainability and long lifespan: Tidal energy facilities typically have a very long operational lifespan.
- Zero carbon: Tidal power generation does not emit any greenhouse gases during operation.
Challenges and Considerations
Alongside its benefits, tidal energy also faces challenges:
- High initial cost: The construction and installation of tidal energy facilities, especially barrages, are very expensive.
- Environmental impacts: Tidal barrages can affect fish migration and coastal ecosystems. Stream generators may also impact marine life.
- Limited suitable locations: Only coastlines with high tidal ranges or strong currents are suitable for the economic exploitation of this energy.
- Maintenance in a marine environment: The salty and corrosive environment of the sea can pose challenges for equipment maintenance.
Global potential and status of tidal energy in Iran
The potential for electricity generation from tides is significant in various coasts around the world, especially in regions like Canada, the United Kingdom, France, South Korea, and Australia. Currently, there are several large-scale tidal energy power plants operating in the world.
In Iran, the southern coasts of the country, especially in the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman, experience tidal phenomena. Although the tidal range in these areas is not as large as in some of the world’s ideal locations, initial studies indicate a limited but considerable potential for utilizing this energy, especially by using tidal stream generator technologies in certain specific locations. There is a need for more comprehensive studies and careful economic and environmental assessments to determine the feasibility of tidal energy projects in Iran.
Conclusion
Generating electricity through tidal power is a powerful and predictable solution for meeting a portion of the world’s future energy needs. Despite challenges such as high costs and environmental impacts, advancements in technology and the increasing demand for clean energy sources have made tidal energy an attractive option in the portfolio of renewable energies. By investing in research and development and selecting suitable locations, we can harness this vast and sustainable resource from the oceans to generate clean electricity and take an important step towards a more sustainable future.