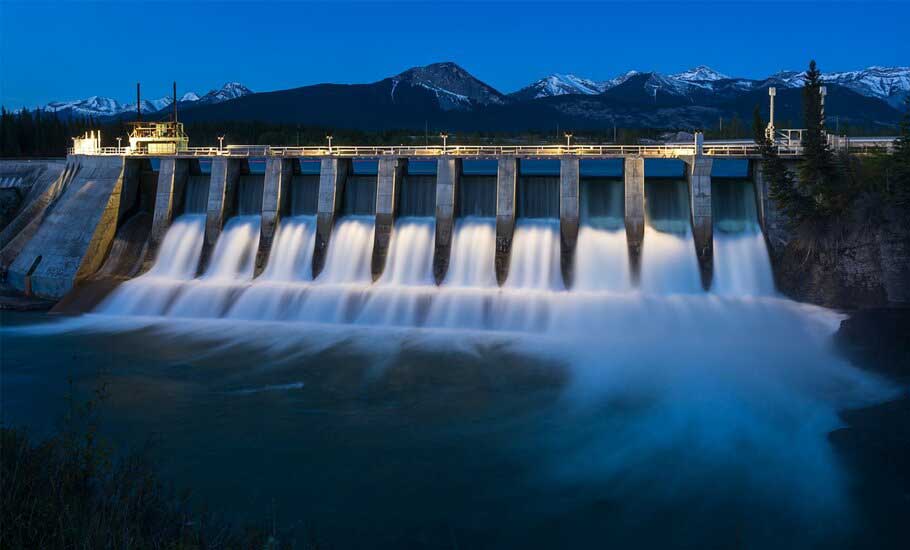
In today’s world, where the focus is on renewable energies, hydropower (or hydroelectricity) holds a special place as one of the oldest and most efficient methods of generating clean electricity. Water, the source of life, is not only essential for daily use, but also has enormous potential to provide sustainable energy on a large scale. But how does hydropower work, and why is this energy source so important? It is a process that generates electrical energy by utilizing the mechanical energy of moving water. Hydroelectric power plants usually extract this energy from the falling water at a height or the rapid flow of water along river paths. Using special equipment, they capture this mechanical energy and convert it into usable electrical energy. The fundamental principle in generating electricity from water is energy conversion: Water stored at a higher elevation (such as behind a dam) possesses significant potential energy. When the power plant releases this water and it flows downward, its potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy (the energy of motion). The plant then uses this kinetic energy to turn the blades of water turbines. The rotation of the turbines, in turn, activates the generators, resulting in electricity production. Hydroelectric power plants are designed and built based on factors such as the topography of the area, the volume of water resources, and operational requirements. The main types of these power plants are: Conventional Hydroelectric Dams Run-of-River Hydroelectric Plants Pumped-Storage Hydroelectric Plants The use of hydroelectricity offers significant advantages: Despite its many advantages, hydroelectricity also comes with challenges and considerations: Hydroelectricity currently holds the largest share among renewable energy sources worldwide and supplies a significant portion of the electricity needed by many countries—especially those with abundant water resources and suitable topography, such as China, Brazil, Canada, the United States, and Norway. In Iran, due to the presence of mountainous regions and a network of rivers, there is significant potential for hydropower generation. Major dams in the country—such as Karun, Dez, Karkheh, and others—not only play a vital role in water resource management, but also make a substantial contribution to the nation’s electricity production. Iran’s hydroelectric power plants form an important part of the country’s energy mix and play a key role in ensuring stable electricity supply. However, the optimal management of water resources and the environmental impacts of dams remain important issues that require ongoing attention and careful consideration. Hydroelectricity, as a clean, renewable, and highly reliable energy source, serves as the backbone of a sustainable energy system in many parts of the world. Despite the challenges related to high initial costs and environmental impacts, technological advancements and modern management approaches are helping to mitigate these effects. By harnessing the natural power of water, hydroelectricity plays a pivotal role in the transition to a lower-carbon future and in meeting the electricity needs of future generations. Our experts at Tose’e Payam Asia will be with you every step of the way—from the construction to the operation of hydroelectric power plants. Resources. International Energy Agency – IEA U.S. Department of Energy – DOE
Hydropower: The Power of Water in Producing Clean and Sustainable Energy
What is hydropower? The conversion of moving water’s energy into electrical energy
Types of Hydroelectric Power Plants
Advantages of Hydropower Energy
Environmental and Social Challenges and Considerations
Global Potential and the Status of Hydropower in Iran
Conclusion
آخرین نوشتهها

Electricity generation through water
زمان مطالعه: 6 دقیقه