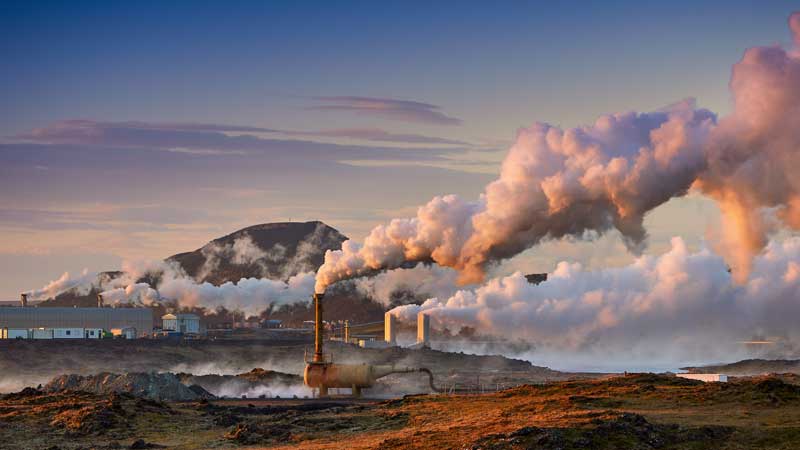
istory of Renewable Energy Use — From the Past to a Clean Future
The longstanding human dependency on nature
For thousands of years, humans have turned to natural resources to meet their needs. Before the discovery and widespread use of fossil fuels, human civilizations derived their energy directly from nature: sunlight for heating, wind for sailing and milling, and flowing water for turning wheels. These resources are the same renewable energies that are once again the focus of attention today. In this article, we take a look at the history of renewable energy use and examine their ups and downs.
Ancient Times: Direct Use of Natural Forces
Early humans knew and utilized natural forces well:
- Solar Energy: People in ancient civilizations built their homes to maximize the use of sunlight and warmth. They used sunlight to dry agricultural products and heat water. The ancient Greeks and Romans used mirrors to concentrate sunlight and generate heat.
- “Biomass energy: Burning wood and plant residues (biomass) is the oldest form of renewable energy use, which humans have leveraged for cooking and heating.
- Wind Energy: Ancient Egyptians used sails to move their boats on the Nile River approximately 5,000 years ago. Later, around the 7th century AD, Iranians built the first windmills for grinding grain and pumping water. This technology rapidly spread throughout the Islamic world and subsequently into Europe.
- Hydropower: Humans have harnessed the force of flowing water since ancient times. The ancient Romans used water wheels for grinding grain. In the Middle Ages, watermills spread throughout Europe, playing a significant role in early industries such as textiles and blacksmithing.
The Industrial Revolution and the Temporary Decline of Renewable Energies
With the onset of the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century, coal emerged as the primary energy source. Steam engines powered by coal offered unprecedented power and flexibility. In the 19th century, oil and then natural gas became the dominant energy sources. These fossil fuels provided concentrated and portable energy that enabled the rapid development of industries and transportation. During this period, the use of traditional renewable energies like wind and water (except on large scales such as hydroelectric dams) was somewhat marginalized.
The 20th Century: Renewed Awakening and New Innovations
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, interest in renewable energy sources re-emerged:
- Modern hydropower: Large dams for generating electricity from water power on a massive scale were constructed, and hydropower became one of the most important energy sources.
- Modern solar energy: In 1883, Charles Fritz built the first solar cell made from selenium. Although its efficiency was very low, it introduced the concept of directly converting sunlight into electricity. In the 1950s, Bell Laboratories developed the first silicon solar cell with significant efficiency, paving the way for subsequent applications.
- Modern wind energy: In the late nineteenth century, the first wind turbines were built to generate electricity. Throughout the twentieth century, the design of wind turbines improved, and their size increased.
- Geothermal energy: The first geothermal power plant began operating in Italy in 1911, utilizing the heat from within the Earth to generate electricity.
Late 20th Century and 21st Century: Rapid Growth and Global Challenges
In the final decades of the 20th century, with increasing concerns about the limitations of fossil fuels and their environmental impacts, countries, researchers, and industries worldwide began to develop and widely utilize renewable energies.
- Technological Advances: Investment in research and development led to significant progress in solar technologies (more efficient and cost-effective photovoltaic panels), wind (larger and more powerful turbines), geothermal, and other sources such as ocean energy.
- Supportive Policies: Governments worldwide supported the development of these resources by providing subsidies, financial incentives, and setting targets to increase the share of renewable energies in their energy mix.
- Cost Reduction: With increased production and technological advancements, the cost of electricity generation from solar and wind sources significantly decreased, making them more economically competitive.
Today, renewable energies are expanding rapidly and play a crucial role in supplying the world’s energy needs. Many countries and companies have set ambitious goals for transitioning to clean energy.
The future is clean energy
The history of renewable energy use shows that humans have always sought to harness the sustainable forces of nature. In the final decades of the twentieth century, the limitation of fossil fuel resources, rising oil prices, and especially the environmental effects of burning them (such as air pollution and climate change) compelled countries and researchers around the world to focus on renewable energies. With technological advances and global support, solar, wind, hydro, and other renewable sources have not only regained their place, but the global community recognizes them as the main pillars of the future energy system, paving the way for a more sustainable and cleaner future. Please go to the Energy Production Resources section to view supplementary videos on the process of renewable energy.